

Unlimited population represents a theoretical model of systems with a large number of possible customers (a bank on a busy street, a motorway petrol station). Population of Customers can be considered either limited (closed systems) or unlimited (open systems). A process that handles the item at the top of the stack first is known as a last-in first-out (LIFO) process.įigure 1 shows the elements of a single queue queuing system: A process that handles queued items from the bottom of the stack first is known as a first-in first-out (FIFO) process. In most systems, an item is always added to the top of a stack. The queues that a computer manages are sometimes viewed as being in stacks. A queue can be studied in terms of: the source of each queued item, how frequently items arrive on the queue, how long they can or should wait, whether some items should jump ahead in the queue, how multiple queues might be formed and managed, and the rules by which items are enqueued and dequeued. In computer science, queueing theory is the study of queues as a technique for managing processes and objects in a computer. In the following you can find more detailled informations for this topic. Examples for the queuing theory are waiting lines in cafeterias, hospitals, banks, airports and so on. Queuing theory analyze the shared facility needs to be accesed for service by a large number of jobs or customers. (Agner Krarup) Erlang, who worked for the Copenhagen Telephone Exchange to find a solution.

This waiting problem leads the Danish engineer A.K. The operation of a multi-server queue, controlled by a sequence $ \ ( t) ) $įor all functionals continuous relative to the uniform metric).It is a common phenomenon in everyday life to see a large number of persons waiting in front of a booking counter, in a railway station or in a theatre or in a ration shop to have some service carried out. The basic definitions and notations are as in Queue.

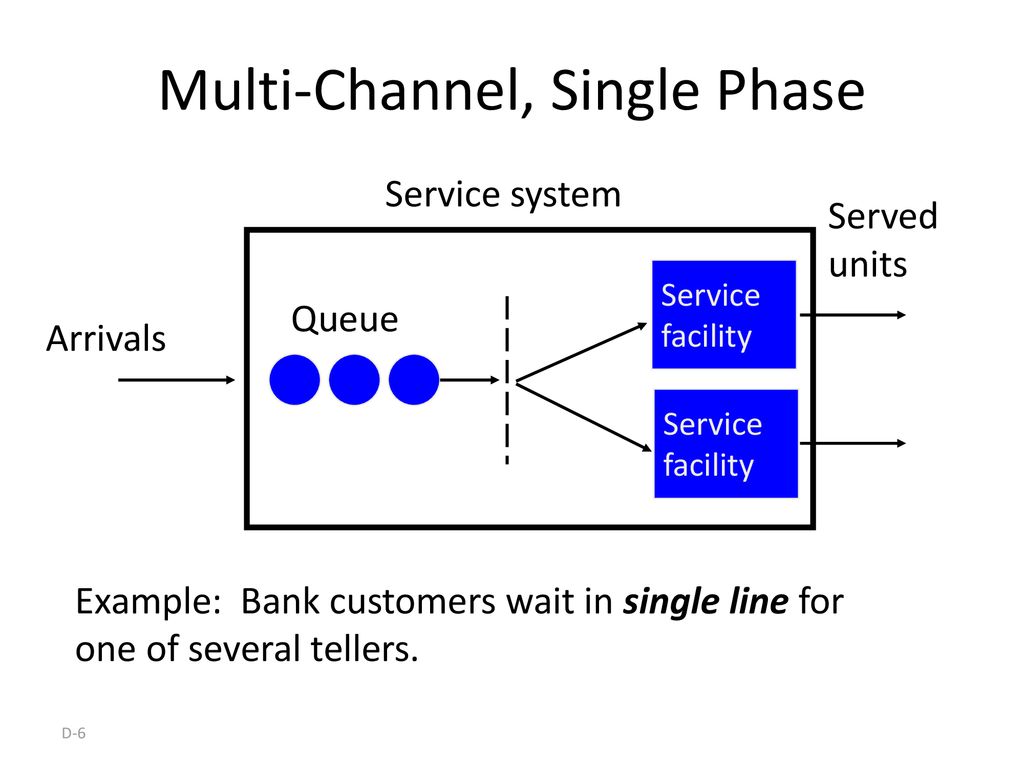
A queue for which the algorithm provides for the calls to form a queue if the system is busy at the time of their arrival here the service of calls takes place in several channels simultaneously.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
